Workflow and process are two terms that are often used interchangeably in business, but they have different meanings and implications. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between workflow and process, and how they can help you improve your efficiency, productivity and quality. We will also share some tips and tools to create and optimize your workflows and processes, and how to measure their effectiveness. By the end of this post, you will have a clear understanding of what workflow and process mean, and how to use them to your advantage. Let’s get started!
- What is a Process?
- What is a Workflow?
- Differences Between a Process and a Workflow
- How to Identify Bottlenecks in Processes and Workflows
- How to Use Processes And Workflows to Maximize Efficiency And Productivity
- Conclusion
What is a Process?
A process is a series of steps or actions that are performed to achieve a specific goal or outcome. A process can be simple or complex, depending on the nature and scope of the goal. For example, a process for making coffee can be as simple as boiling water, adding coffee grounds, and pouring the brew into a cup. A process for launching a new product can be more complex, involving multiple departments, tasks, resources, and deadlines.
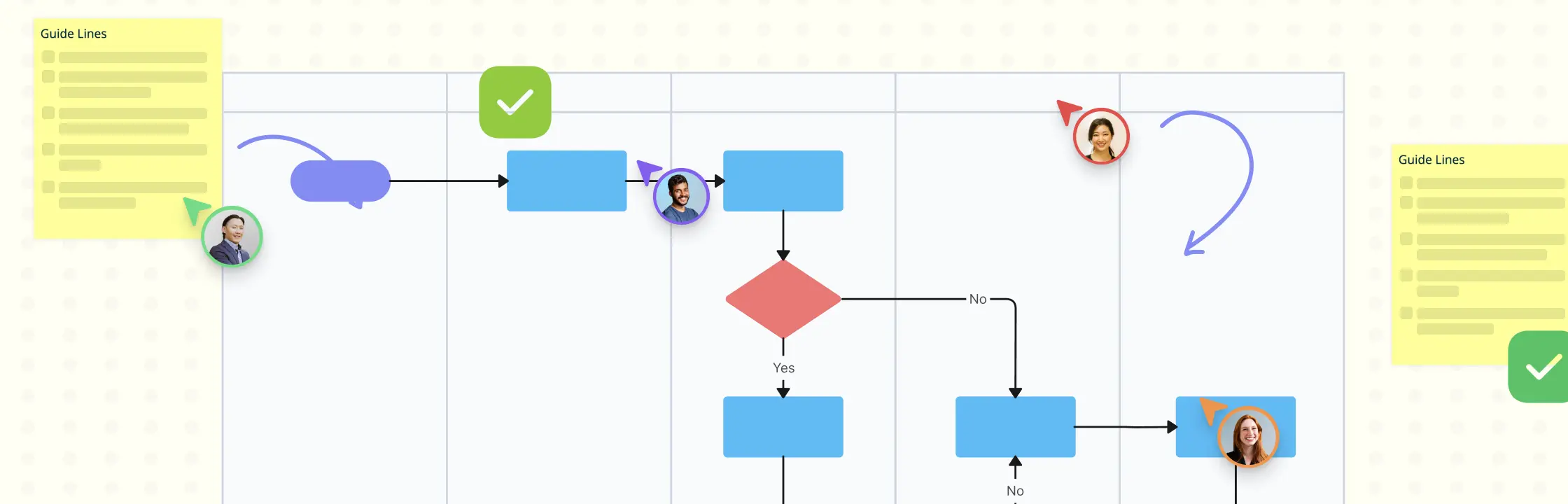
What is a Workflow?
A workflow is a visual representation of a process. It shows the sequence and flow of the steps or actions, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the people involved. A workflow can be created using diagrams, charts, or software tools. A workflow helps to clarify and communicate the process, as well as to monitor and improve its efficiency and effectiveness. For example, a workflow for making coffee can show who is responsible for boiling water, adding coffee grounds, and pouring the brew into a cup. A workflow for launching a new product can show the dependencies and timelines of each task and department.
Differences Between a Process and a Workflow
| Process | Workflow |
|---|---|
| An abstract concept that describes what needs to be done to achieve a goal | A concrete representation that shows how the process is done |
| Focuses on the logic and order of the steps or actions | Focuses on the execution and coordination of the steps or actions |
| Can exist without a workflow | Cannot exist without a process |
| Can be performed without a visual aid | Requires a visual aid to be created and followed |
Templates that Can Help Create Workflows
Flowchart
BPMN Diagram
Activity Diagram
Fishbone Template
Kanban Board
How to Identify Bottlenecks in Processes and Workflows
A bottleneck is a point in a process or workflow where the flow of work slows down or stops due to an obstacle or constraint. A bottleneck can cause delays, errors, waste, frustration, and customer dissatisfaction. Some common causes of bottlenecks are:
- Lack of resources: such as staff, equipment, materials, or budget.
- Lack of clarity: such as unclear roles, responsibilities, instructions, or expectations.
- Lack of communication: such as poor feedback, collaboration, or information sharing.
- Lack of alignment: such as conflicting goals, priorities, or standards.
To identify bottlenecks in your processes and workflows, you can use the following steps:
-
Map out your current process or workflow: using diagrams, charts, or software tools.
-
Analyze each step or action: using data, metrics, or feedback.
-
Identify where the flow of work slows down or stops: using indicators such as waiting time, queue length, utilization rate, or error rate.
-
Determine the root cause of the bottleneck: using techniques such as brainstorming, root cause analysis, or fishbone diagram.
-
Implement solutions to eliminate or reduce the bottleneck: using methods such as automation, delegation, simplification, standardization, or optimization.
How to Use Processes And Workflows to Maximize Efficiency And Productivity
Efficiency and productivity are two key measures of business performance. Efficiency refers to how well you use your resources to produce your outputs. Productivity refers to how much you produce with your inputs. Processes and workflows can help you maximize both efficiency and productivity by:
- Streamlining your operations: by eliminating unnecessary or redundant steps or actions.
- Enhancing your quality: by reducing errors or defects.
- Increasing your speed: by shortening cycle times or lead times.
- Improving your consistency: by following best practices or procedures.
- Boosting your collaboration: by facilitating teamwork or coordination.
- Empowering your employees: by providing clear guidance or feedback.
To use processes and workflows to maximize efficiency and productivity, you can use the following steps:
- Define your goals and objectives: using SMART criteria (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound).
- Design your processes and workflows: using tools such as flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or business process modeling notation (BPMN).
- Implement your processes and workflows: using tools such as project management software, workflow management software, or business process management software (BPMS).
- Monitor your processes and workflows: using tools such as dashboards, reports, or analytics.
- Improve your processes and workflows: using tools such as surveys, audits, or reviews.
Conclusion
Processes and workflows are essential for any business that wants to achieve its goals and objectives. By understanding the difference between them, and how to use them effectively, you can optimize your operations and improve your performance. Remember, a process is a series of steps or actions that are performed to achieve a specific goal or outcome. A workflow is a visual representation of a process that shows the sequence and flow of the steps or actions, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the people involved. To identify bottlenecks in your processes and workflows, you can map out your current process or workflow, analyze each step or action, identify where the flow of work slows down or stops, determine the root cause of the bottleneck, and implement solutions to eliminate or reduce the bottleneck. To use processes and workflows to maximize efficiency and productivity, you can define your goals and objectives, design your processes and workflows, implement your processes and workflows, monitor your processes and workflows, and improve your processes and workflows.
We hope you found this blog post helpful and informative. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
FAQs About Workflows and Processes
Some examples of processes and workflows in different industries are:
- Manufacturing: a process for producing a product, such as assembling parts, testing quality, or packaging. A workflow for managing inventory, such as ordering supplies, storing materials, or delivering goods.
- Healthcare: a process for providing care to a patient, such as diagnosing symptoms, prescribing treatment, or monitoring recovery. A workflow for managing records, such as collecting data, storing information, or sharing reports.
- Education: a process for delivering education to a student, such as designing curriculum, teaching lessons, or assessing learning. A workflow for managing administration, such as enrolling students, scheduling classes, or issuing grades.
Some benefits of using processes and workflows in your business are:
- Increased customer satisfaction: by delivering faster, better, and more consistent products or services.
- Reduced costs: by saving time, money, and resources.
- Enhanced innovation: by enabling creativity, experimentation, and improvement.
- Higher employee engagement: by providing clarity, direction, and motivation.
Some challenges of using processes and workflows in your business are:
- Resistance to change: by facing inertia, fear, or skepticism from stakeholders.
- Complexity: by dealing with multiple variables, dependencies, or exceptions.
- Adaptability: by coping with changing customer needs, market conditions, or technology trends.