Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standard for visualizing and designing business processes. It uses various symbols to represent different elements in a process. Here is a complete list of BPMN symbols along with their meanings.
Check out our guide on BPMN to learn about the Business Process and Modeling Notation in more detail.
What are BPMN Symbols
BPMN symbols are graphical elements used in BPMN diagrams to represent various aspects of business processes. These symbols provide a standardized and visual way to document, analyze, and communicate complex workflows and activities within an organization. BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) symbols can be categorized into several main types based on their functions in visualizing business processes.
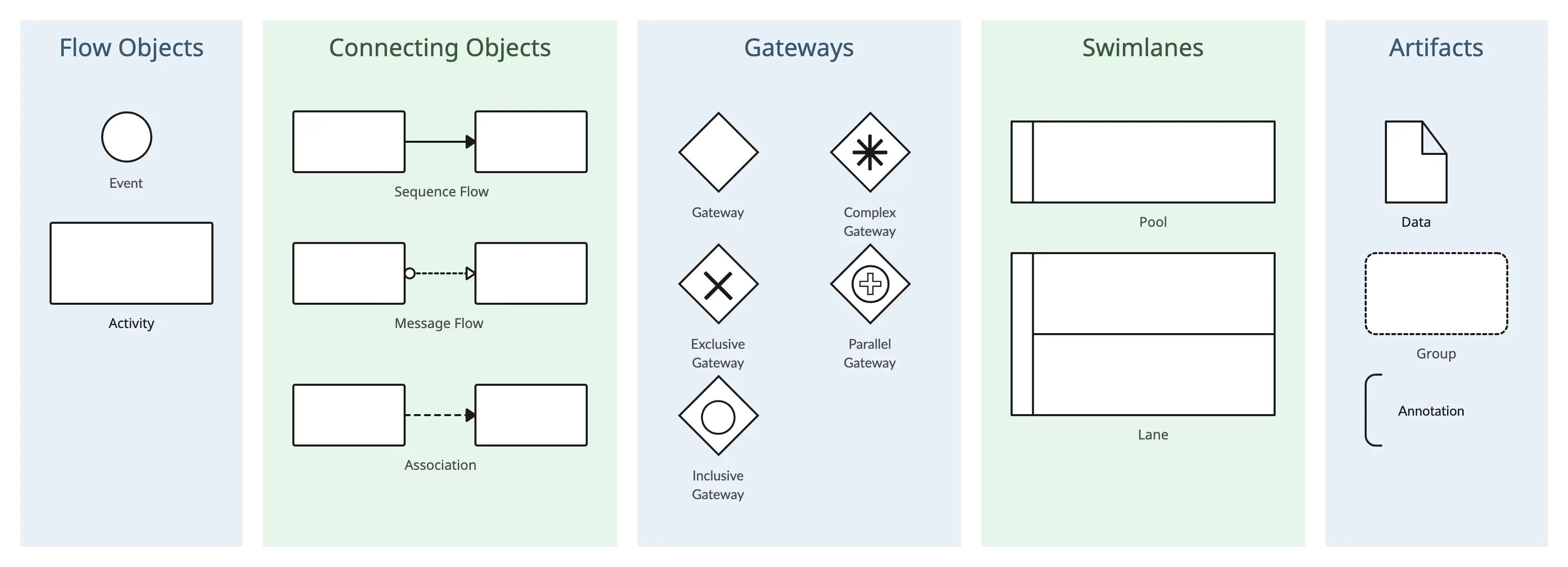
1. Flow Objects in BPMN
Flow objects are symbols that represent elements in a business process that impact the flow of the process. They collectively help model the sequence of activities, events, and decision points within a business process. They provide a clear representation of how the process flows and the conditions or events that trigger different actions.
Events
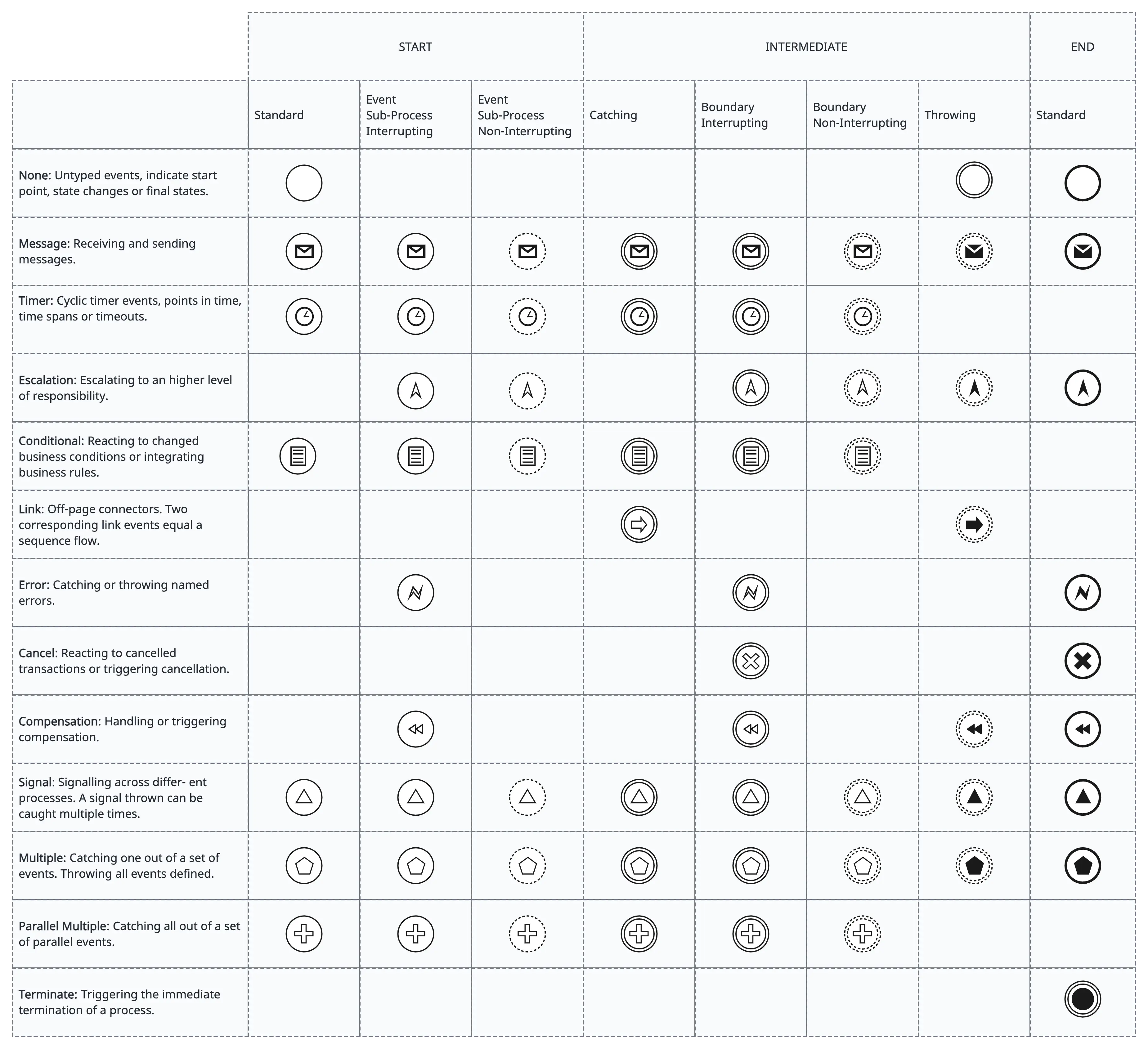
Events are key elements that represent occurrences or states within a business process. Events play a crucial role in modeling the flow of activities and defining how the process responds to external stimuli or triggers. There are three main types of BPMN events: Start Events, Intermediate Events, and End Events.
Start Events
Start events mark the beginning of a process. They represent the points at which a process is initiated. There are several types of start events, including:
- None start event: The process starts immediately without an external trigger.
- Message start event: The process is triggered by the receipt of a message.
- Timer start event: The process is initiated based on a predefined time or timer.
- Conditional start event: The process starts based on a specified condition.
- Signal start event: The process begins in response to the receipt of a signal.
- Multiple start events: Multiple events can trigger the start of the process, and any one of them can initiate the process.
Intermediate Events
Intermediate events occur between the start and end of a process. They represent points where something happens during the execution of the process.
- Message intermediate event: Represents the receipt or sending of a message during the process.
- Timer intermediate event: Represents an intermediate point in the process based on a timer or specific time.
- Conditional intermediate event: Represents an intermediate point based on a specified condition.
- Signal intermediate event: Represents the occurrence of a signal during the process.
- Link intermediate event: Represents the use of a link to connect different parts of the process.
- Compensation intermediate event: Represents the initiation of compensation activities in case of an error or exception.
- Error intermediate event: Represents an error condition during the process.
End Events
End events mark the conclusion or completion of a process. They represent the points at which the process finishes its execution. There are several types of end events, including:
- None end event: The process concludes without any specific result.
- Message end event: The process concludes by sending a message.
- Error end event: The process concludes with an error condition.
- Terminate end event: The process is terminated abruptly.
- Signal end event: The process concludes in response to a signal.
- Multiple end event: Multiple end events can be used to indicate various possible outcomes or results.
Activities
Activities are represented by various symbols to depict different types of work or tasks within a business process. The main BPMN activity symbols are:
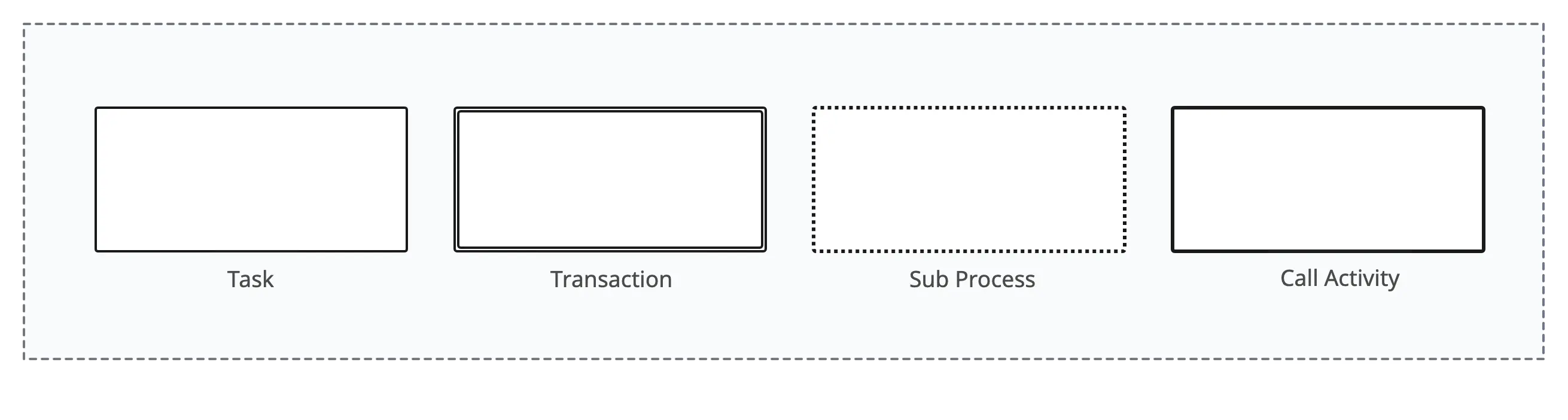
- Task: Represents a unit of work that needs to be performed as part of the process. Tasks can be atomic (indivisible) or expanded into sub-processes.
- Sub-process: Represents a subprocess within the main process. Subprocesses allow for the decomposition of complex processes into smaller, more manageable components.
- Transaction: Represents a transactional subprocess, which is a specialized form of a subprocess. It makes sure that all enclosed activities are completed successfully or rolled back in case of an error.
- Call activity: Represents a call to a global process or a reusable subprocess defined outside of the current process. It is used for modularizing processes and reusing them in different contexts.
Activity Markers
Activity markers are symbols or icons added to BPMN activity shapes to convey additional information about the nature or behavior of the activity.
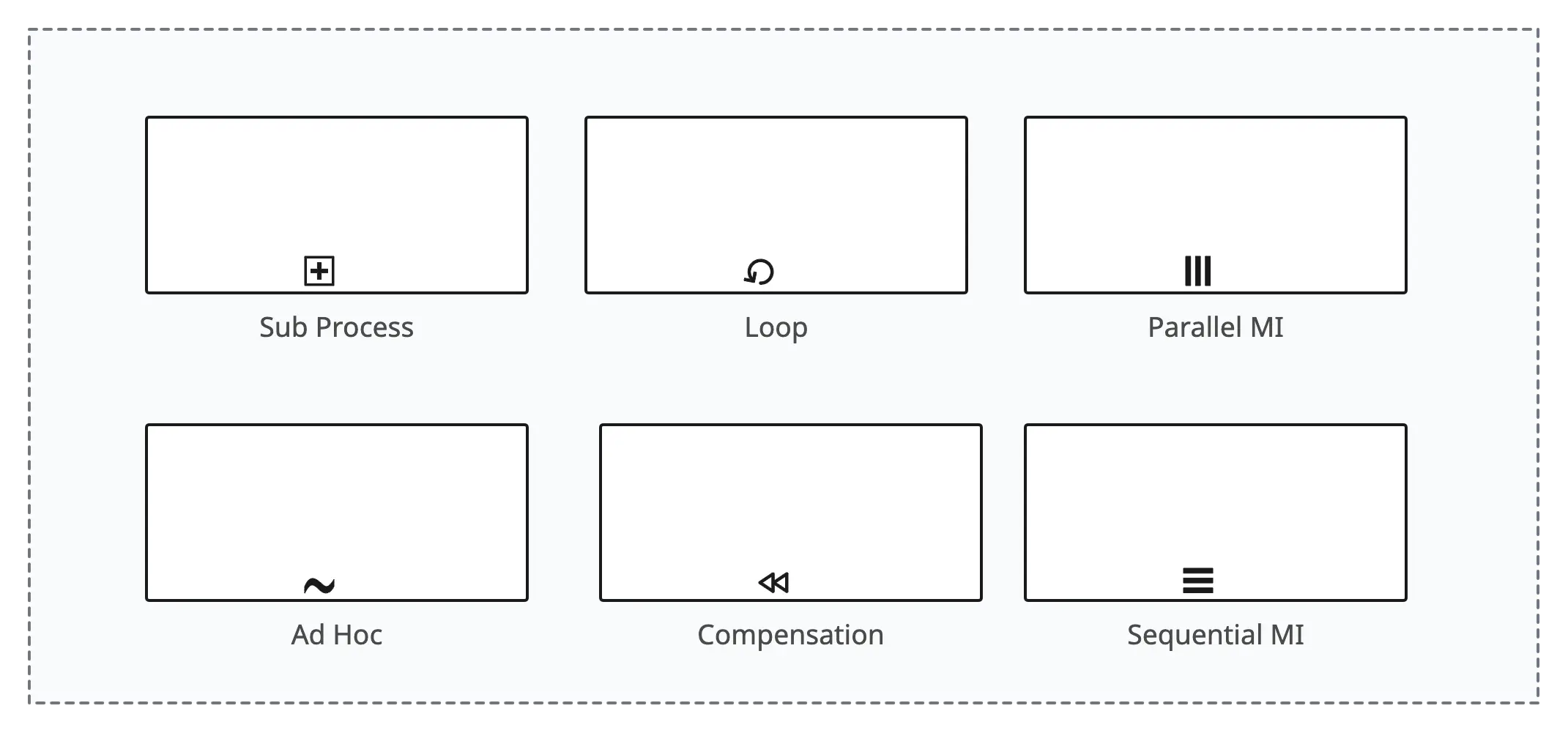
- Loop marker: Indicates that the associated activity or subprocess should be repeated in a loop until a certain condition is met.
- Parallel marker: Indicates that the tasks within a subprocess can be executed in parallel.
- Ad hoc marker: Indicates that the tasks within the subprocess can be performed in any order or repeated as needed.
- Compensation marker: Indicates that the activity is a compensation activity, and it is associated with handling compensation for a previous activity in case of an error.
- Sequential marker: Indicates that the tasks within a subprocess should be executed sequentially.
Task Types
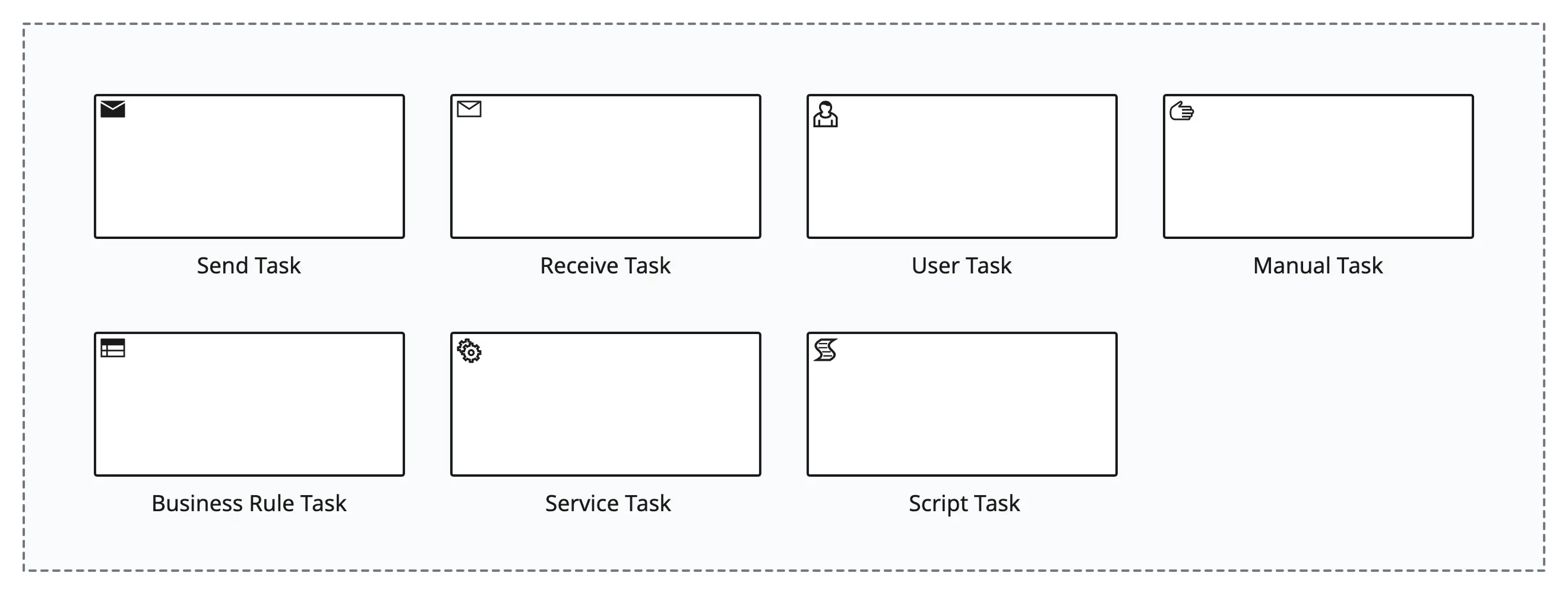
- Send task: Represents a task that sends a message or signal to another process or participant.
- Receive task: Represents a task that waits for a message or signal to be received before proceeding.
- User task: Represents a task that requires human interaction. It is typically performed by a knowledge worker or end-user.
- Manual task: Represents a task that is performed manually by a human, but it is less specific than a User Task.
- Business rule task: Represents a task that is based on business rules or decision logic. It is often used for decision-making within the process.
- Service task: Represents an automated task that is performed by a software service or system. It may involve communication with external systems.
- Script task: Represents a task that is performed based on a predefined script or script language. It is typically automated.
2. Gateways
BPMN gateways are symbols used to model decision points and control the flow of a business process. Gateways determine which path the process should take based on certain conditions or events.
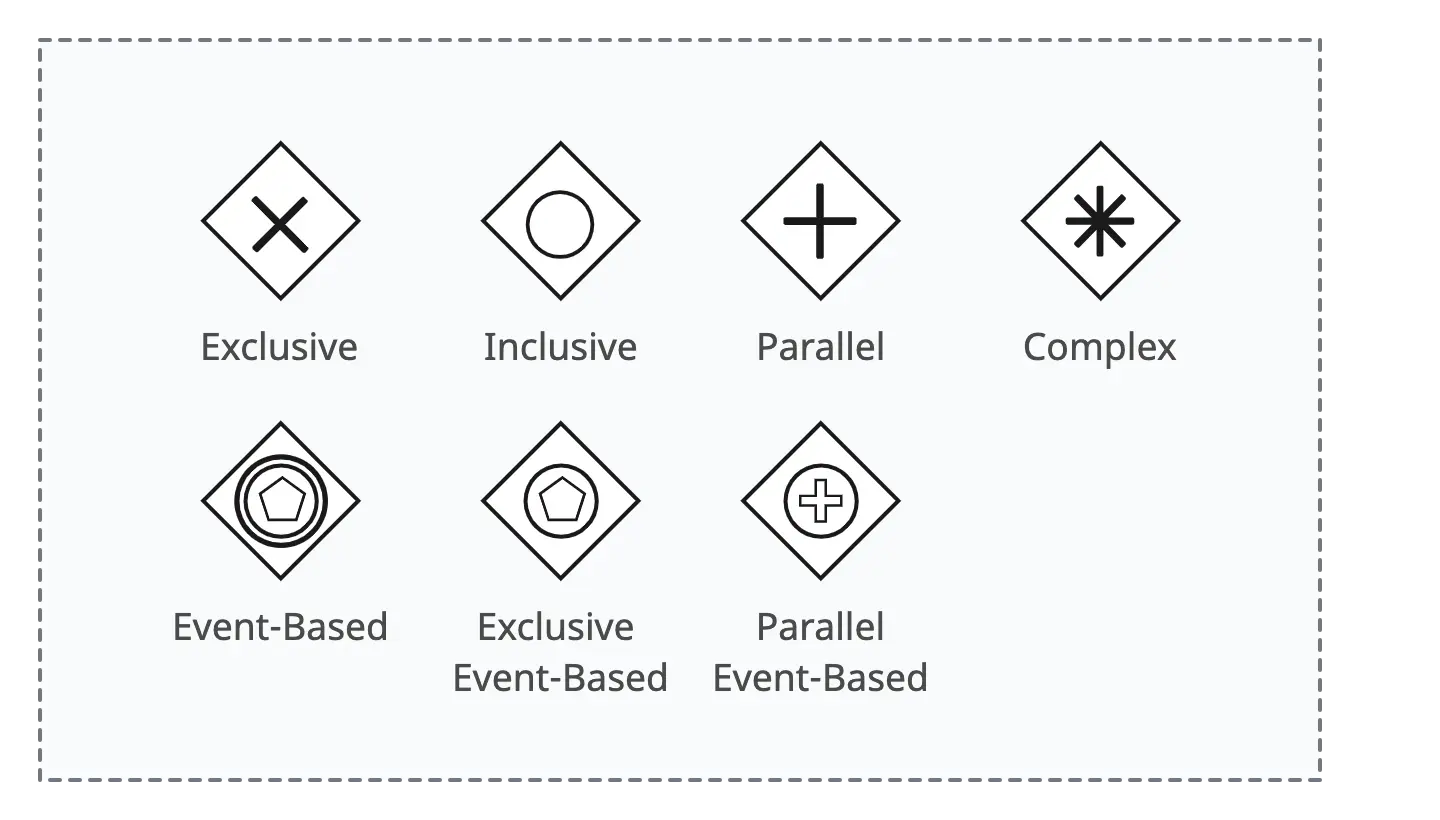
- Exclusive gateway: Represents a decision point where only one of the outgoing paths can be taken. The decision is based on evaluating conditions associated with each outgoing sequence flow.
- Inclusive gateway: Represents a decision point where multiple paths can be taken based on evaluating conditions associated with each outgoing sequence flow. All paths with true conditions are taken.
- Parallel gateway: Represents a point where multiple paths can be taken simultaneously without evaluating conditions. It is used for parallel execution of activities.
- Complex gateway: Represents a more complex decision point where conditions and rules may involve a combination of logical operators. It allows for more sophisticated decision-making logic.
- Event-based gateway: Represents a decision point based on events. It is used when the process flow depends on the occurrence of specific events, such as receiving a message or a timer event.
- Exclusive event-based gateway: Similar to the event-based gateway, but enforces exclusive decision-making based on events. Only one path can be taken, depending on the first event to occur.
- Parallel event-based gateway: The occurrence of all subsequent events starts a new process instance.
3. Artifacts
Data Symbols
Data symbols represent the flow and handling of data within a business process. They help in visualizing how data is created, used, stored, and transferred throughout the process.
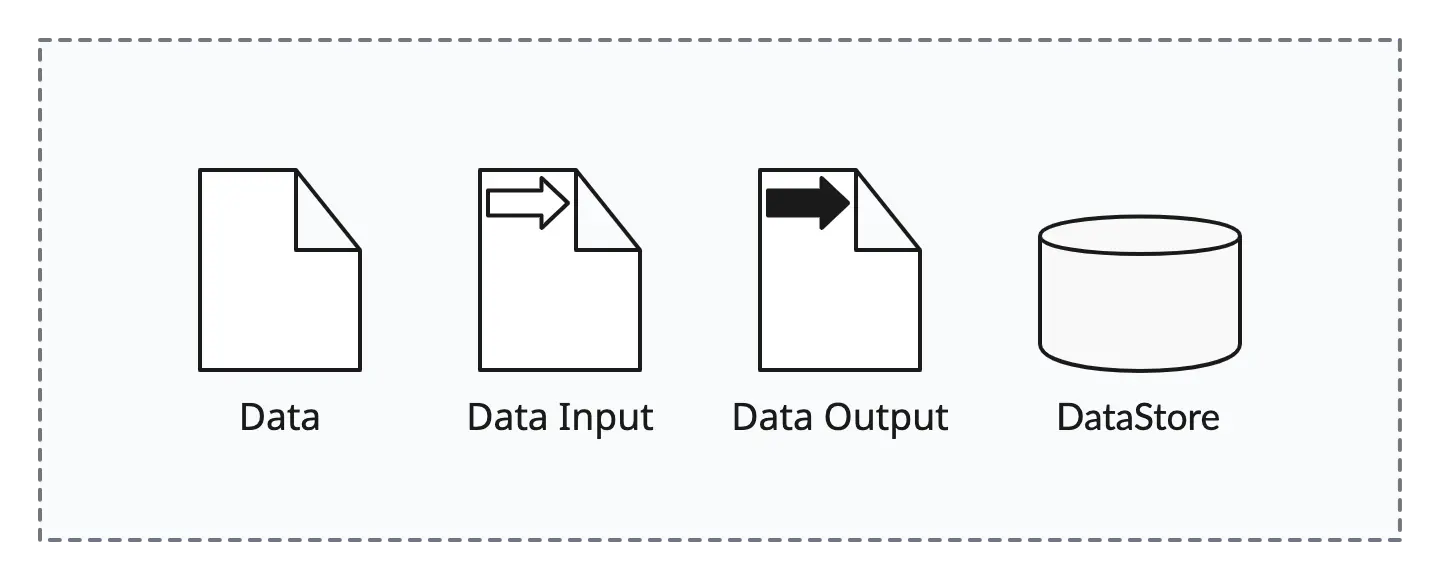
- Data object: Represents data or information used or produced within a process. It helps illustrate the flow of data between activities.
- Data input/output: Represents the input or output of data from an activity. It indicates the flow of data into or out of a task or subprocess.
- Data store: Represents a place where data is stored during the execution of a process. It can be a physical repository or a database.
Group, Annotation, & Association
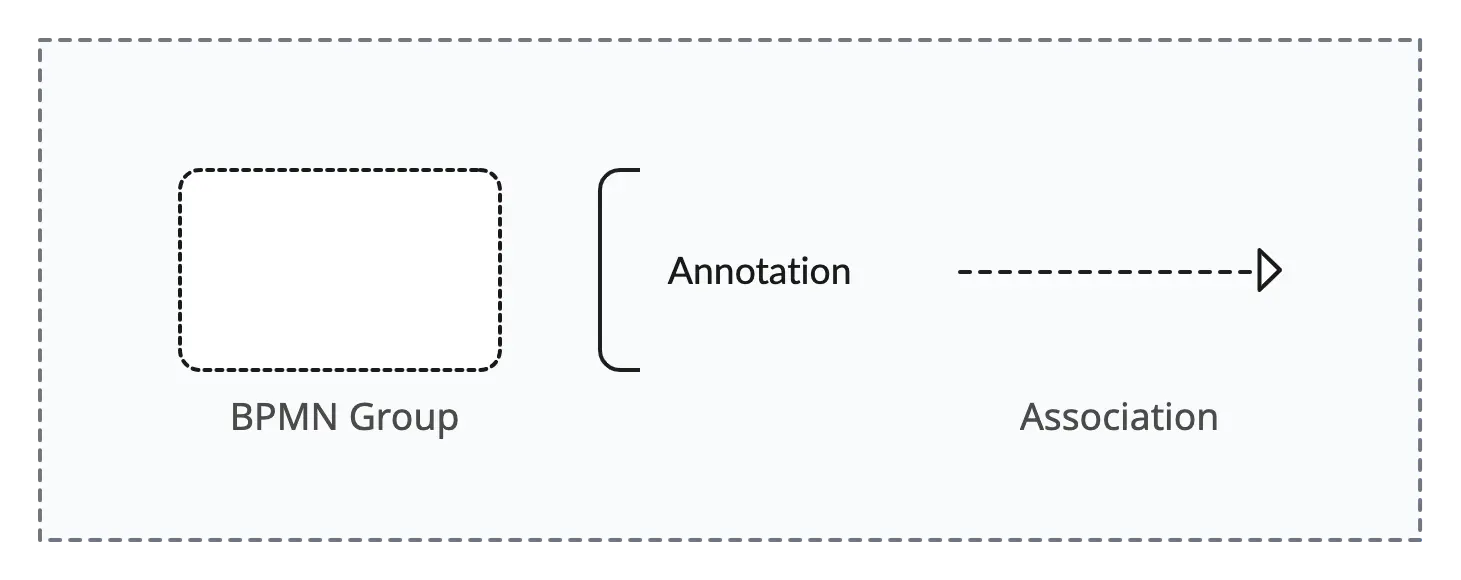
- Group: Groups related elements in a diagram. It is often used to visually organize and highlight specific sections of the process.
- Annotation: Provides additional information or comments to enhance the understanding of the process. Annotations are often used to add explanatory notes or documentation.
- Association: Connects artifacts, data objects, or text annotations to flow objects, indicating a relationship or dependency. Associations help in clarifying connections between elements.
4. Conversations
Conversations are used to model interactions and communications between participants in a business process. Conversations provide a high-level view of how different participants, typically represented as Pools in BPMN diagrams, exchange messages and collaborate to achieve a common goal.
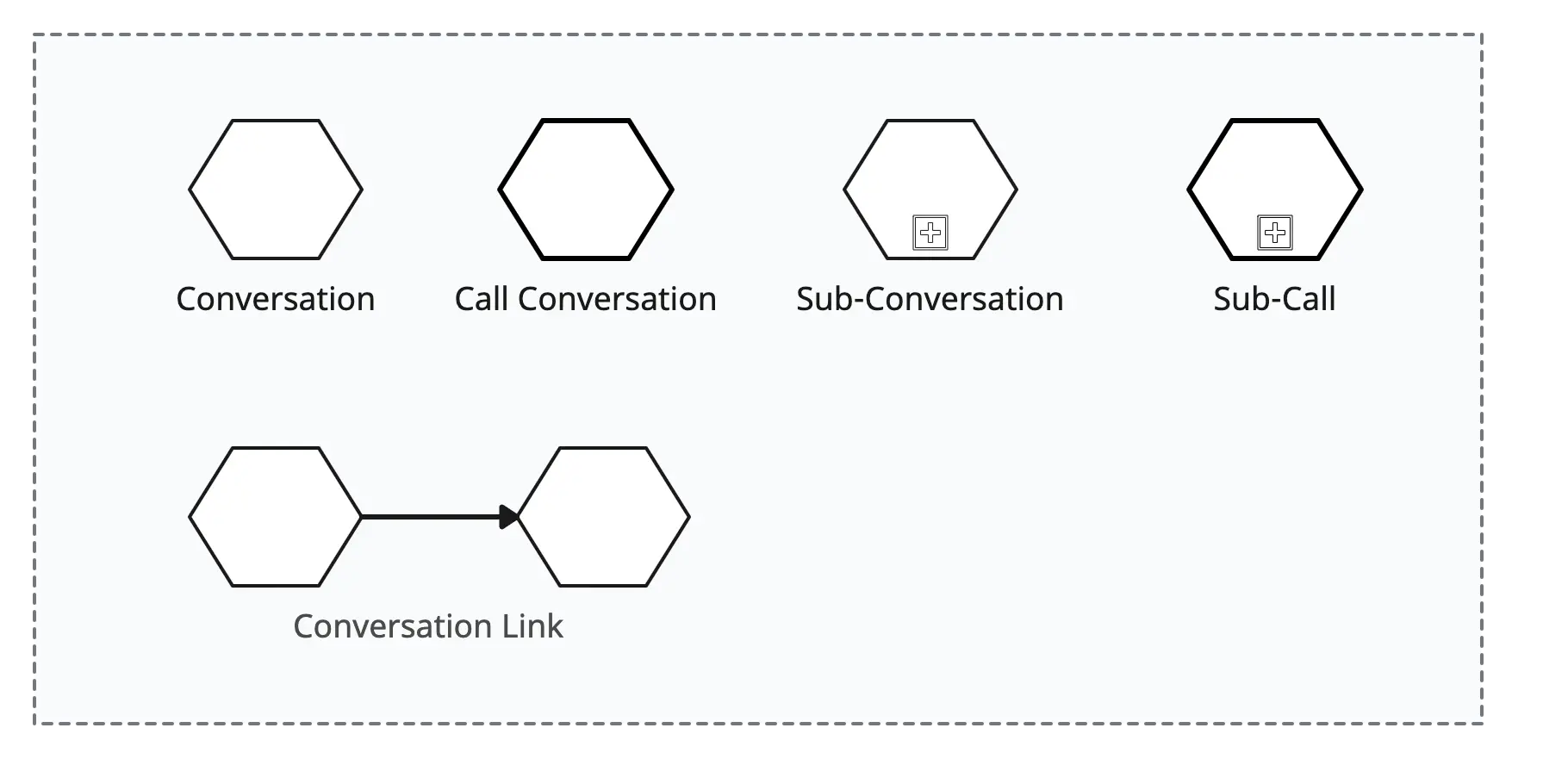
- Conversation: Represents a conversation or communication between different participants in a business process. It provides an overall context for the interactions.
- Sub-conversation: Represents a more detailed or nested conversation within a larger conversation. It is used to provide a more granular view of interactions within a specific part of the overall process.
- Call conversation: Represents a call or sub-process that is initiated from within a conversation to represent a more detailed interaction or subprocess.
- Conversation link: Represents a connection or link between different parts of a conversation or between different participants. It indicates that there is a relationship or interaction between them.
5. Connecting Objects
Connecting objects are symbols used to illustrate the relationships and connections between different elements within a business process. These connecting objects help define the sequence, flow, and dependencies among various BPMN elements.
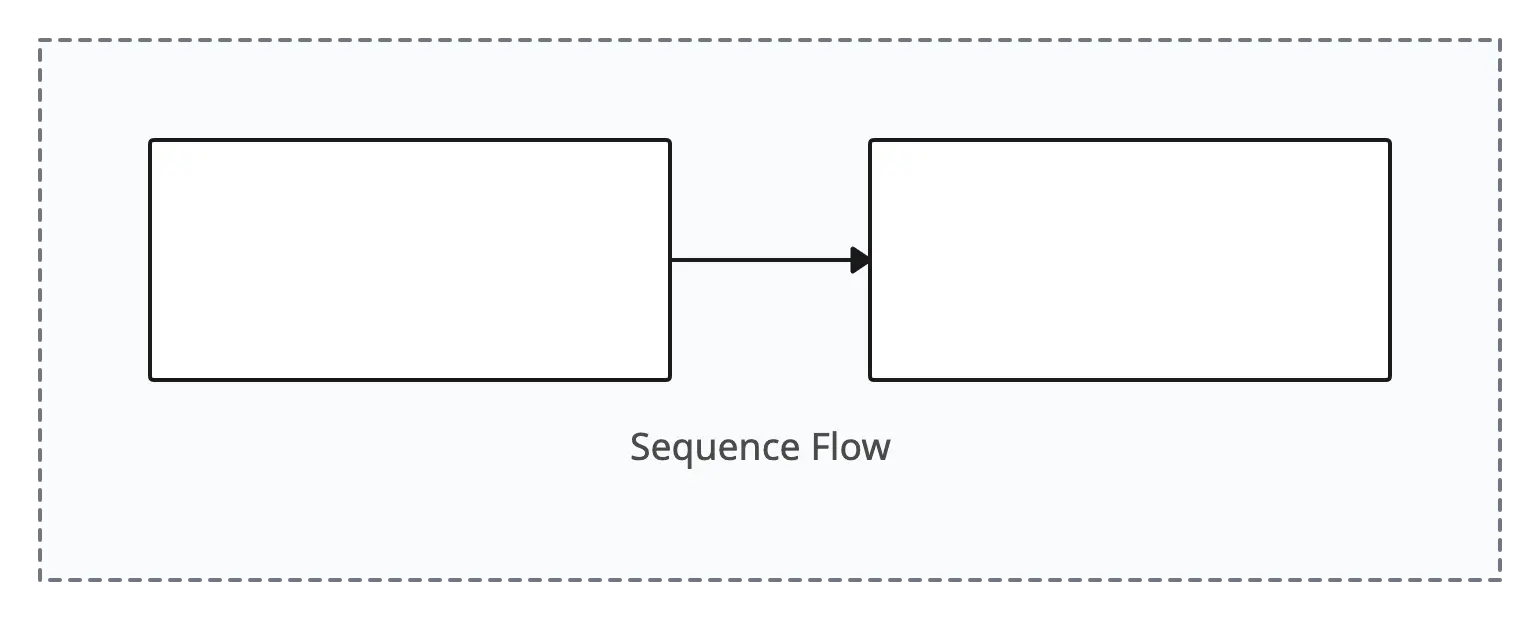
Sequence Flow
Represents the order in which activities or events are performed within a process. It connects two flow objects, indicating the direction of process flow.
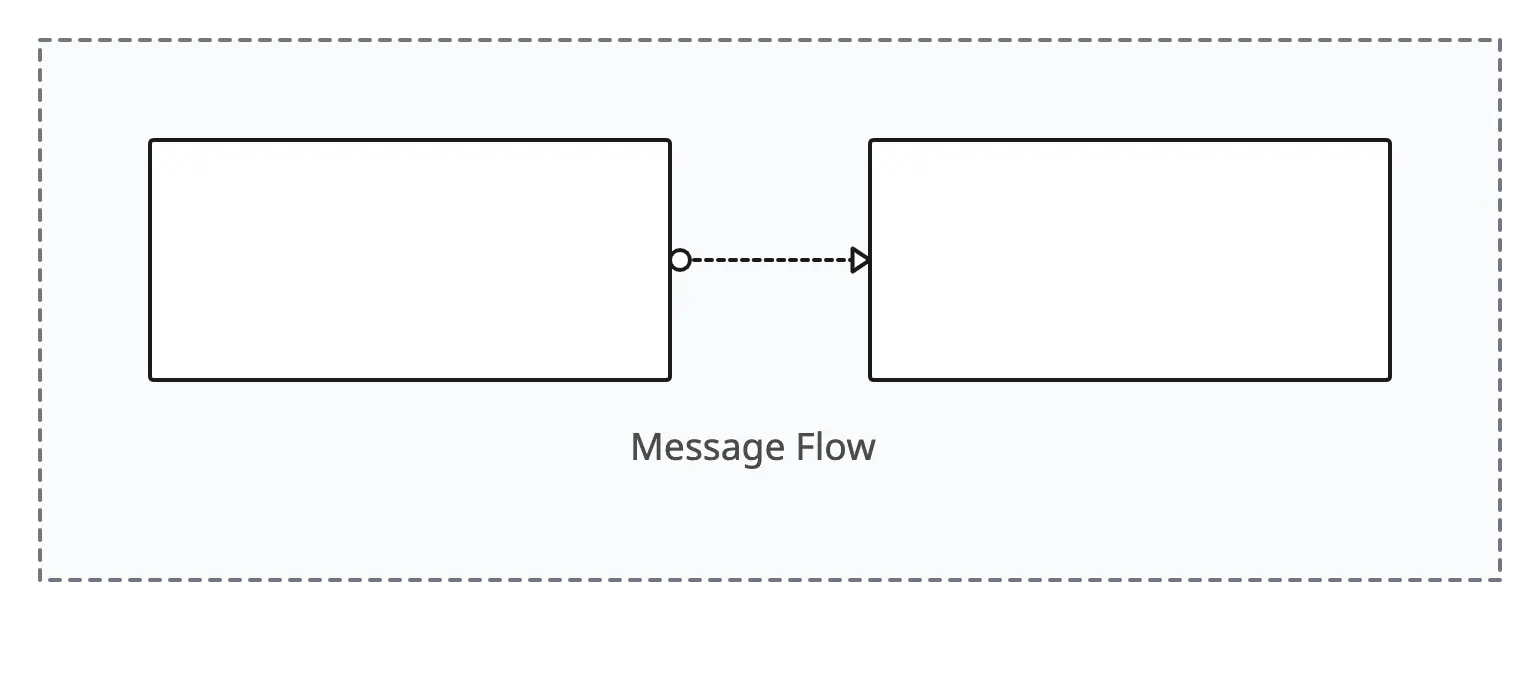
Message Flow
Represents the flow of messages between participants or pools in a process. It illustrates the communication paths between different entities.
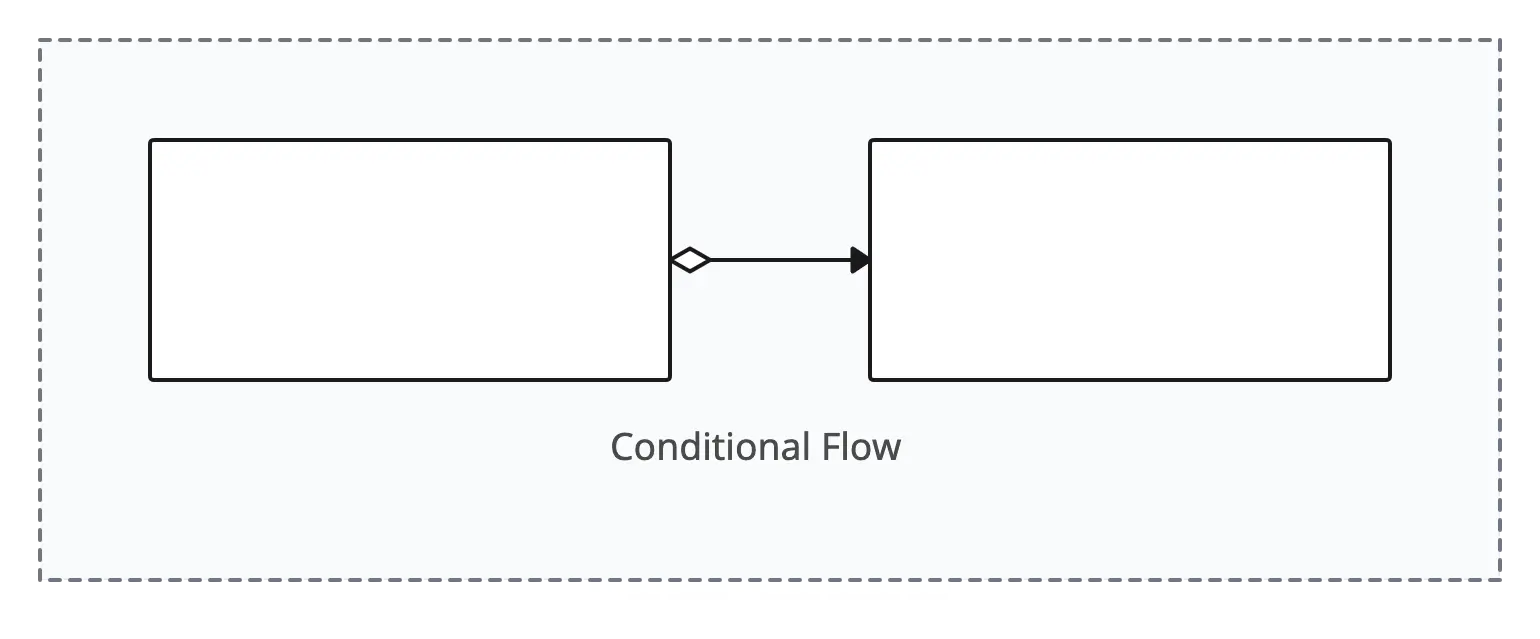
Conditional Flow
Represents a flow in the process that is taken based on a specific condition or decision.
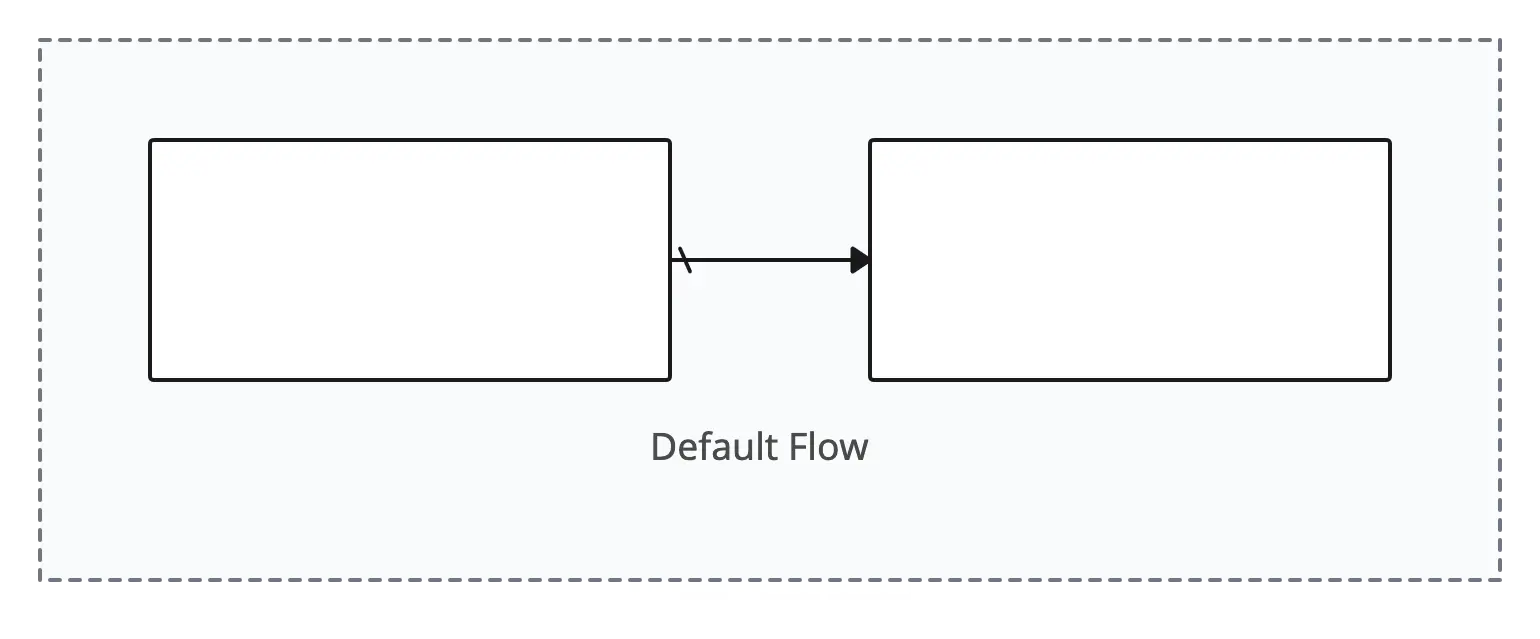
Default Flow
Default flow is the default branch to be chosen if all other conditions evaluate to false.
6. Swimlanes
Swimlanes are used to visually organize and categorize activities within a business process. Swimlanes are typically represented as horizontal or vertical partitions that divide the process diagram into sections, each corresponding to a specific participant, role, department, or system involved in the process.

Pools
Pools are used to represent separate organizational entities or participants in a process. Each pool can contain its own set of activities and processes, and communication between pools is depicted using message flows.
Lanes
Lanes are subdivisions within a pool and are used to organize and categorize activities further. Each lane typically corresponds to a specific role, department, or system within the organizational entity represented by the pool.
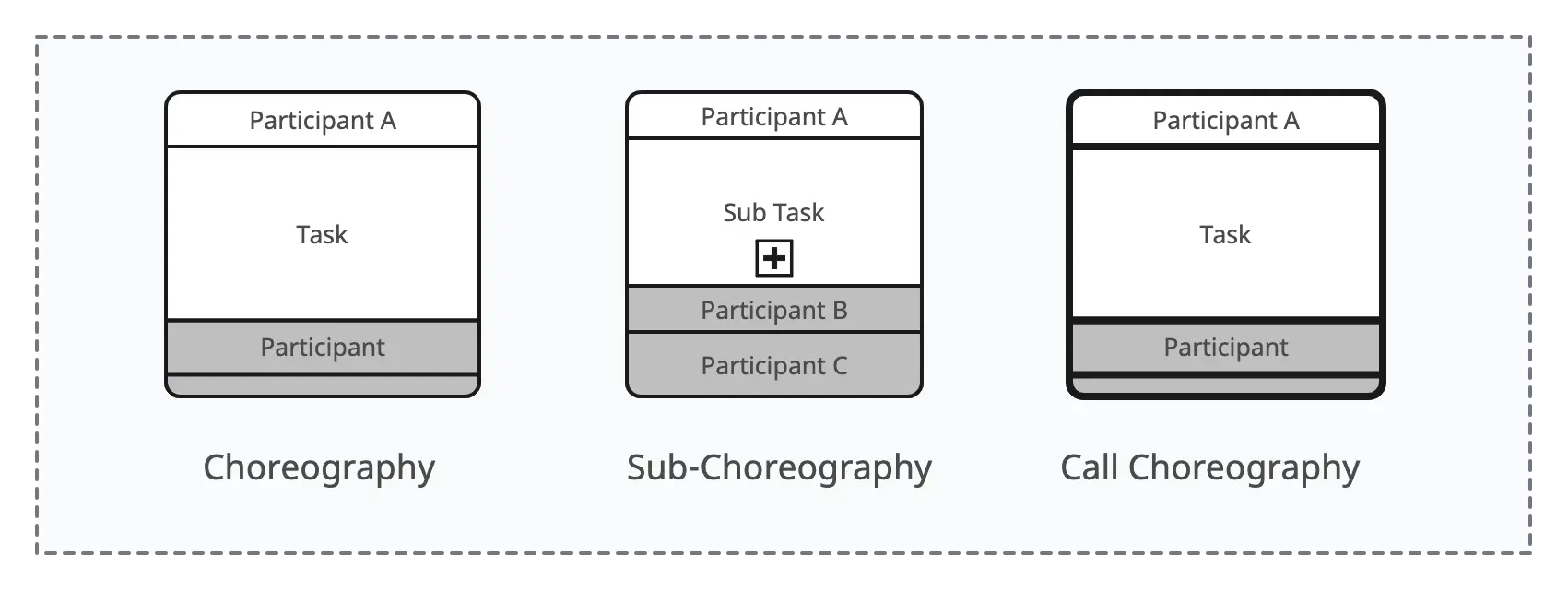
7. Choreographies
Choreographies provide a way to model the interactions and collaborations between multiple participants or entities in a business process. Unlike traditional process diagrams that focus on the internal workings of a single participant, choreographies emphasize the communication and coordination between different entities.
Use BPMN Symbols with Creately
Now that you have a comprehensive idea of all the BPMN symbols, get started on creating a BPMN diagram. Creately offers a complete shape library of standard BPMN 2.0 shapes listed above for you to create accurate BPMN diagrams to represent your business processes. Effectively streamline visualizing processes with your team with Creately’s intuitive drawing tools and real-time collaboration.